Each year, hundreds of thousands of people in the U.S. suffer traumatic brain injuries. According to the American Association of Neurological Surgeons, an average of 288,000 people are treated for traumatic brain injuries in the hospital each year, and 13.5 million Americans are living with disabilities caused by TBIs. Getting prompt treatment is important when a TBI is suspected. Early treatment might help to improve recovery and make the prognosis better. Understanding the signs of a traumatic brain injury and seeking a proper diagnosis might help the victims to recover faster so that they can return to their normal routines.
What is a traumatic brain injury?
According to Los Angeles brain injury attorney Steven M. Sweat, traumatic brain injuries are closed-head injuries that happen when the brain’s tissue forcibly contacts the bones of the skull. The brain is surrounded by fluid to help to cushion it. When something forcefully strikes the head are causes violent movements of the head and neck, the brain can strike the inside of the skull and be damaged. For people younger than age 44, traumatic brain injuries are the leading causes of death in the U.S. These injuries can range in severity. People who suffer severe TBIs may be left with debilitating injuries that last for the rest of their lives.
What are the signs of a traumatic brain injury?
After an accident, it is important for people to recognize the signs that someone might have suffered a traumatic brain injury. If you see that someone is displaying some of the following symptoms after an accident, you should seek immediate medical help:
- Depression
- Confusion
- Severe headache
- Loss of memory
- Difficulty maintaining balance
- Dizziness
- Extreme tiredness or fatigue
- Nausea
- Sleep disturbance
- Difficulty concentrating
- Light or noise sensitivity
In severe cases, people who suffer traumatic brain injuries may experience seizures or fall into comas. Seeking prompt medical care can prevent the damage from worsening.
Common causes of traumatic brain injuries
Traumatic brain injuries can happen whenever someone suffers a blow to the head or encounters forces that cause their heads to violently accelerate and decelerate in the same direction. TBIs are common in motor vehicle accidents and sports. Many people have likely read about professional football players who have suffered from serious TBIs and have been left with disabilities. Falls are another common cause of TBIs. According to data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, falls are the leading cause of traumatic brain injuries. Fall accidents account for 35.2% of TBIs, and older adults ages 75 and older and children ages 0 to four have the greatest risks. People also suffer traumatic brain injuries in assaults.
How traumatic brain injuries are diagnosed
When someone suffers a traumatic brain injury, his or her condition can quickly worsen. This makes it important to treat a suspected TBI as an emergency and to promptly seek medical care.
Doctors may use several tools to diagnose traumatic brain injuries. The Glasgow Coma Scale might be administered by doctors or other emergency medical professionals. This scale tests the ability of the victim to perform simple tasks and is rated on a scale of three to 15. Scores that are higher indicate less severe injuries.
If someone else witnessed the accident, the doctors may ask them questions about the injury to help the medical professionals determine its severity. You might be asked how the injury happened, whether the victim lost consciousness, and other questions about the various symptoms that you observed.
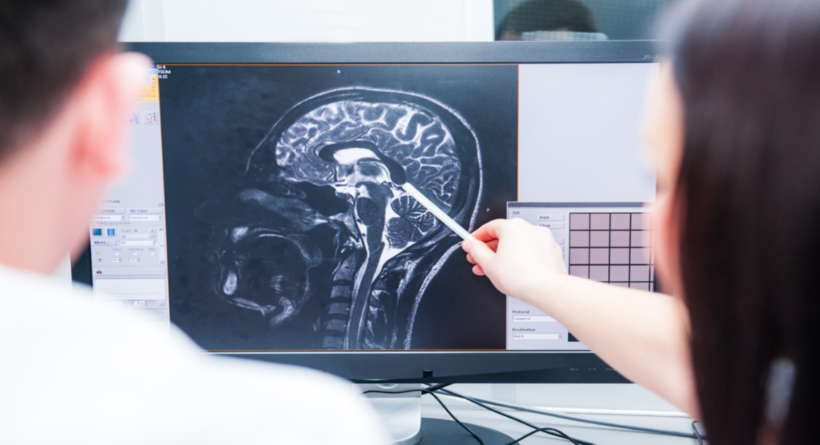
The doctors may also use imaging scans to diagnose a traumatic brain injury. A computerized tomography or CT scan may be completed soon after the victim arrives in the emergency department when a traumatic brain injury is suspected. A CT scan offers a quick way for doctors to see any broken bones, hemorrhages, brain swelling, contusions, and other damage. Once a person’s condition has stabilized, the doctors may then use magnetic resonance imaging to get a detailed image of the brain.
Treatment of traumatic brain injuries
If there is the pressure caused by excess fluid, doctors may relieve the intracranial pressure to prevent further damage by inserting a drainage tube. Doctors might insert a monitor to check the pressure on the brain.
The treatment that might be used for traumatic brain injuries will depend on their severity. People who suffer mild TBIs may be told to rest at home and to take over-the-counter medications to relieve pain. However, their conditions should be monitored at home. If they worsen, they should return to their doctors.
People who suffer moderate to severe traumatic brain injuries will need more aggressive treatment. In the emergency department, people with moderate to severe TBIs may need interventions to ensure that they are getting enough oxygen and blood flow. The doctors may focus on preventing secondary injuries caused by a lack of oxygen or blood to the brain, inflammation, or bleeding.
Several medications may be administered to prevent further damage, including the following:
- Diuretics to reduce pressure on the brain
- Anticonvulsants to prevent seizures
- Drugs to induce comas so that the brain can function with less oxygen temporarily
Emergency surgery may also be required for people who suffer severe TBIs. These surgeries might include surgeries to repair broken bones and to remove bone fragments, surgeries to remove hematomas that are placing pressure on the brain, surgeries to stop brain bleeds, and surgeries to reduce the intracranial pressure by inserting tubes to drain excess fluid.
Following emergency treatment, most people who suffer moderate or severe TBIs will require rehabilitation. Rehabilitation for TBI patients is focused on helping them to relearn skills so that they can perform the basic activities of daily life. The length and type of rehabilitation will depend on the severity of the injury and the specific symptoms that the victims suffer. There are many different types of rehabilitation specialists that might be involved, including vocational and occupational rehabilitation experts, psychiatrists, physical therapists, speech therapists, social workers, recreational therapists, and others.
While traumatic brain injuries are fairly common, they can permanently change the course of people’s lives. Recognizing the signs of traumatic brain injuries and seeking prompt medical care is important for improving the prognosis for recovery. Getting properly diagnosed and treated might prevent further damage from happening and allow people to recover so that they can move forward with their lives. When the injuries are severe, the treatment may be ongoing and expensive. However, people who suffer traumatic brain injuries because of the actions of others might be able to recover damages to pay for their losses by filing legal claims.
Laila Azzahra is a professional writer and blogger that loves to write about technology, business, entertainment, science, and health.